First of all, I have a question for you; have you ever used a service provided by a virtual assistant?Perhaps you have searched for a route through a map app with your smartphone’s voice assistant? Have you ever used a cleaning robot to sweep your house? If you answered yes to any of these questions, you have already been in contact with artificial intelligence (AI).
The study and development of systems that exhibit some human-like intelligence is a fascination that has attracted researchers and scientists for a long time. In this article, you will be introduced to the idea of genuine intelligence and how cognitive computing systems have evolved over the years to assist with the acceleration of your business’ results.
Artificial intelligence is almost everywhere
With the advancement of technology, this theme is increasingly widespread and applications that use artificial intelligence algorithms are much more present in the services we use and products we buy than we realize. It may not be so noticeable, but there are many different kinds of intelligent system in the world around us. We can find them in medicine, security, transport, food, entertainment, the work market, connected home appliances, as well as many other areas.
According to a study carried out by a startup, there is a fairly balanced scenario when it comes to AI startups for this year in Brazil. You can see this in the highlighted areas, which are health and technology (12.5%), HR (10%), agriculture (9.6%), industry 4.0 (9.6%).
By 2025, the cumulative income from artificial intelligence resources will reach billions of dollars. Image recognition and classification systems will reach more than $8 billion, while algorithmic performance-enhancing technologies will surpass $7.5 billion.
What is genuine intelligence?
A simple definition of genuine intelligence is that it is the intelligence of living beings. Therefore, bringing this idea to computational systems would mean to say that a genuinely intelligent system would be a system which presents a form of learning similar to our own. It is also important to mention that cognitive computing represents computational systems that try to imitate the way our brain works, using reasoning, vision and speech for example.
The evolution of cognitive computing systems
The search for the creation of machines capable of reproducing our own intelligence dates back to ancient Greece. In the 19th and 20th centuries, with the advent of studies by George Boole, Charles Babbage, Ada Lovelace and Alan Turing, among other great names, it was already possible to create machines capable of making surprising calculations and which, later, would give rise to the development of artificial intelligence. In truth, the field of AI was formally founded in 1956, in the so-called Dartmouth Conference in the USA, and from there, specific research in the area began.
With regard to artificial intelligence systems with cognition, some contemporaries of philosophical thought had great influence, such as Watson and Skinner’s Behaviorism. It consisted of analyzing the behavior of individuals and their interaction with the environment, corresponding to classical conditioned stimuli and response.
Learning by reinforcement
To better understand what learning by reinforcement is and how it works, imagine that an individual (the player) is interacting with an environment (the game) through trial and error, and they receive a reward or loss as feedback for each action.
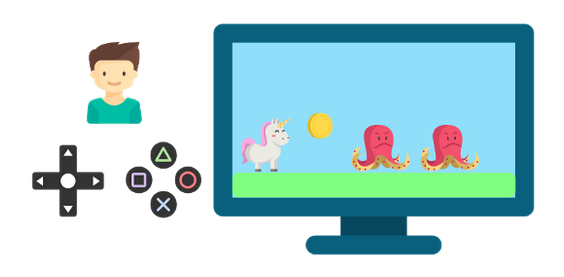
So, as the environment sends a current state or “frame” to the player, they will have to make a decision or “action”, which in turn can generate a positive reward if he gets a coin, or a negative reward if he touches a monster for example.
Research in AI used the same idea of having an autonomous agent interacting with an environment, receiving positive or negative reinforcement for its actions. This is a specific field of machine learning, which is learning by reinforcement using neural networks.
Smart agents in real life
According to the systems analyst at Atlantico, Paulo Jarbas Camurça, with the continued advancements in the computational power of new processors and graphics processing units (GPUs), large companies have used reinforcement learning in the development of intelligent agents, that are capable of interacting with board games and electronics. These machines have even beat the world’s best. Paulo goes on to say “Here we can mention the famous chess game of Kasparov vs. Deep Blue, also the game of GO, with Lee Sedol vs. Deep Mind, and not to mention the battles between AI and DOTA (Defense of the Ancients) players.”.
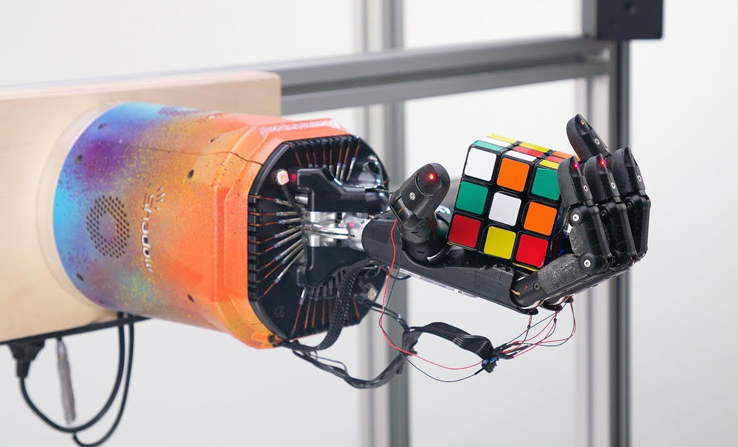
Another field that has benefited greatly is robotics, with applications in control and automation, such as the robotic hand developed by Open AI, that is capable of solving a Rubik’s Cube, in addition to the increase of research in the area of health.
According to Jarbas, machine learning models that are able to learn through contexts such as natural language and speech are increasingly being used. “There is already an AI from Google that can perform everyday tasks, such as calling people, sending messages and even making reservations at a restaurant. Other real examples are Tesla, who develops autonomous vehicles, and SpaceX, which has already produced rocket capsules that return to their base entirely alone. Fantastic, isn’t it?”, comments Paulo Jarbas.

For nearly 20 years, Atlantico has been anticipating the future of the information and communication technology market. It has been doing this through the adoption of new technologies in business, such as the integration of digital technologies in all areas, allowing the exploration of growth, optimization, innovation and new possibilities.
The cognitive computing platform comprises a portion of the artificial intelligence area that works with systems, and algorithms and research inspired by human cognitive processes and carried out by machines. This is one of Atlantico’s areas of expertise.
*Content developed in partnership with Atlantico’s system analyst, Paulo Jarbas Camurça.







